In today’s world, electric vehicles account for approximately two percent of auto sales, and that number only continues to grow. Now, electric semi-trucks and freight vehicles, or commercial battery-electric vehicles (CBEVs), are merging onto America’s roads and highways. Manufacturers have poured billions of dollars into developing CBEVs, and companies are slowly integrating the new technology into their fleets. And while the focus has mainly been on Class 8 trucks, automakers are introducing commercially available models in numerous classes.
So, what exactly does this electric revolution look like and who is responsible?
Who are the key creators of electric semi-trucks?
Very few automakers dared to venture into the world of EV manufacturing. However, those who did are now reaping the benefits of their investment. Currently, Volvo Trucks offers two tractor configurations for their electric Class 8 trucks, including a 4×2 and a 6×2. These trucks provide different ranges that are dependent on the amount of cargo you’re hauling and the overall size of your trailer. The manufacturer also sells an electric box truck model, which offers a range of 150 miles on a single charge.
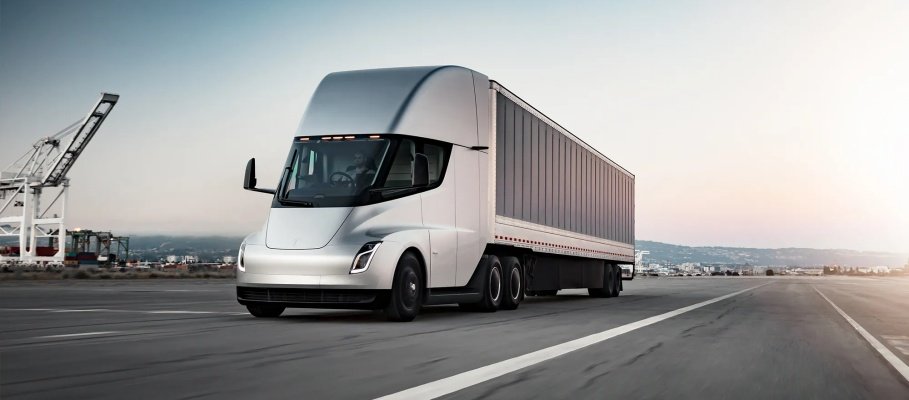
And in 2021, Volvo received its largest order from Quality Custom Distribution (QCD) for its VNR Electric model. The foodservice logistics supplier ordered a total of 14 electric trucks for their Southern California drivers. While the new EVs won’t significantly impact QCD’s original fleet of 700 fuel-powered trucks, it’s a step in the right direction. Daimler has also been a key player in the EV market with models like the Freightliner eM2 and Freightliner eCascadia. And while Volvo and Daimler have been innovators in the trucking industry’s EV movement, Tesla has recently unveiled what may be the new standard in trucking…
Check out the reveal of the new Tesla Semi
How will electric semi-trucks shape the future of trucking?
Experts from the U.S. Energy Information Administration estimate that battery-electric trucks will account for 31% of the industry or reach around 672 million vehicles by 2050. Undeniably, this would reshape the trucking industry and the world as we know it.
In a single day, a fuel-powered truck will be on the road for up to 11 hours, all while producing harmful emissions. And if a team of drivers runs the truck, it could be on the road even longer. But, if a company were to deploy just one EV, it would be equivalent to placing over a dozen electric sedans on the road, thus significantly reducing harmful emissions.
The North American Council for Freight Efficiency (NACFE) created Run on Less – Electric, a trucking demonstration that set out to determine the pros and cons of EVs. The run further confirmed that CO2 and particulate emissions would be significantly reduced by replacing traditional trucks with electric ones.
Electric trucks also reduce noise pollution and provide optimal safety through intuitive technology and design measures. For instance, the Tesla Semi is built with active safety features that help to prevent jackknifing. Volvo Trucks also attempts to provide enhanced safety through a new, patented safety feature called Active Grip Control. The feature “improves stability, acceleration, and braking in slippery conditions.”
What concerns come with battery-electric trucks?
While there are clear advantages to using BEVs, there are some concerns.
The main concerns include:
- The effects of extreme weather and temperatures on electric trucks.
- Maintenance costs and schedules.
- Availability of parts and services.
- The overall safety of electric trucks.
Thankfully, some testing and trial runs have shed light on the above mentioned issues. The NACFE’s Run on Less – Electric found that extreme weather and temperatures don’t pose any serious threats to BEVs’ overall performance or vitality.
RoL-E also proved that overall maintenance costs and failure rates are less than internal combustion vehicles. However, when the microchip and automotive technology shortage struck the nation in 2020, many EV manufacturers found themselves between a rock and a hard place. Automakers were not only unable to produce new electric models, but they weren’t able to make most of the necessary parts or components. This led many owner-operators to question whether or not moving to BEVs would be wise, considering the unpredictability of the future.
What should fleets keep in mind moving forward?
Before fleets commit to transitioning to BEVs, there are a few things that fleet managers and owner-operators should keep in mind, including:
- How many miles are being driven?
- How often would charging need to take place for each truck?
- Will charging stations or at-home charging need to be installed?
- How many BEVs would be needed?
- Would a partial conversion make more sense than replacing the entire fleet? Or vise-versa.
Fleet managers must also consider a maintenance plan for their electrified fleet. Industry experts who’ve made the move recommend “[getting] your mechanics in there and [getting] them trained” in the new-age technology. Finally, if owner-operators choose to transition to CBEVs, they must implement proper safety protocol and invest in new safety equipment, including arc lash shields, dielectric boots/shoes, electrical safety gloves, insulated tools, etc.
More Like This:
→ Self-Driving Semis: The Future of the Trucking Industry
→ What Truckers Need to Know About Autonomous Vehicles
→ Autonomous Vehicles: What Does it Really Mean?