Whether you’re an experienced driver or new to the industry, conducting a complete inspection before every trip protects you, your vehicle, your cargo, and your business.
A proper inspection helps you identify mechanical issues early and avoid roadside violations that can damage your Compliance, Safety, Accountability (CSA) score or lead to out-of-service orders.
This ultimate semi-truck inspection checklist is designed to help truckers stay ahead of issues, maintain industry compliance, and ensure every component of your truck and trailer is working properly before hitting the road.
By paying close attention to the details outlined below, you’ll be better prepared for daily operations and long-haul demands.
Why Semi Truck Inspections Matter
Semi truck inspections prevent breakdowns, improve safety, reduce costly repairs, and keep you compliant with Department of Transportation (DOT) and Federal Motor Carrier Safety Administration (FMCSA) regulations.
Semi trucks can weigh up to 80,000 pounds, and when a component fails at that scale, the consequences can be serious: accidents, cargo damage, missed delivery windows, unexpected downtime, and potential liability problems for the driver and carrier.
Routine inspections help you:
- Identify wear and damage before they become mechanical failures
- Verify fluid levels, gauges, hoses, and brake components are in safe operating condition
- Stay compliant with FMCSA and avoid fines, penalties, and out-of-service orders
- Maintain complete and accurate inspection records for audits and roadside checks
- Protect your income by reducing preventable breakdowns and roadside delays
- Extend the life of critical components, including brakes, tires, suspension, and the engine compartment
By paying close attention to both the truck and trailer before every trip, you ensure safer driving conditions, strong reliability, and long-term performance for your vehicle and business.
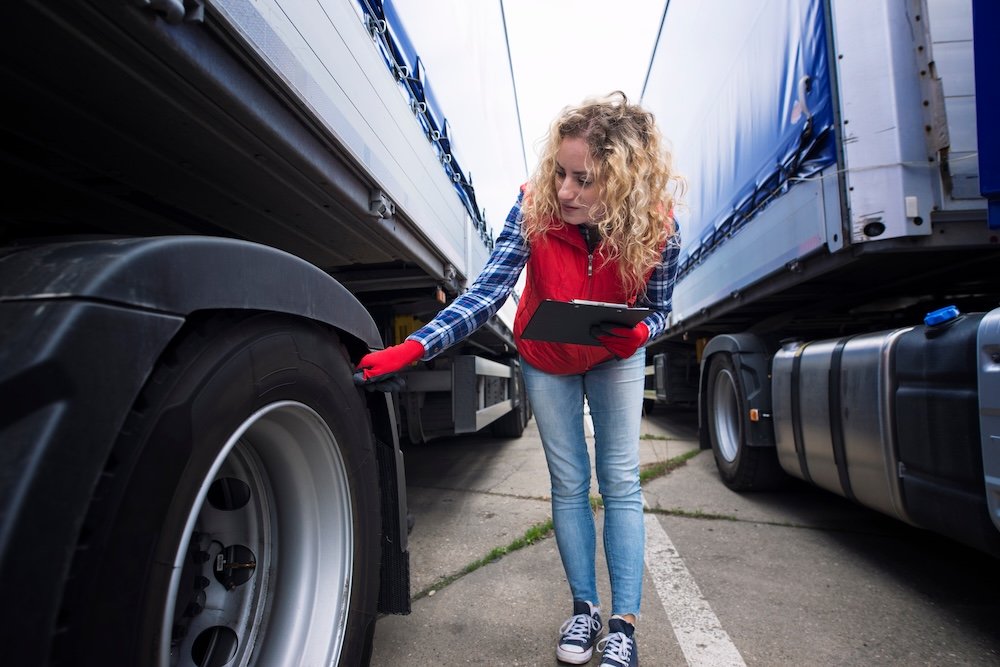

Complete Semi Truck Inspection Checklist
Before you pull out of the yard, run through this commercial truck checklist to confirm nothing is missing or damaged.
1. Exterior Walkaround
Perform a complete exterior walkaround to verify the truck’s overall condition. An exterior walkaround helps you spot early signs of mechanical issues before they turn into costly repairs or safety problems.
Check each item individually:
- Inspect mirrors, windows, and the windshield for cracks, chips, loose mounts, or missing seals.
- Ensure doors, hinges, and latches open and close properly.
- Confirm steps, grab handles, and fenders are secure and free of damage.
- Check hood latches, hood alignment, and surrounding panels for proper fit.
- Examine frame rails, crossmembers, and exterior body panels for corrosion or structural damage.
- Verify reflective tape, DOT markers, and reflectors are intact and clearly visible.
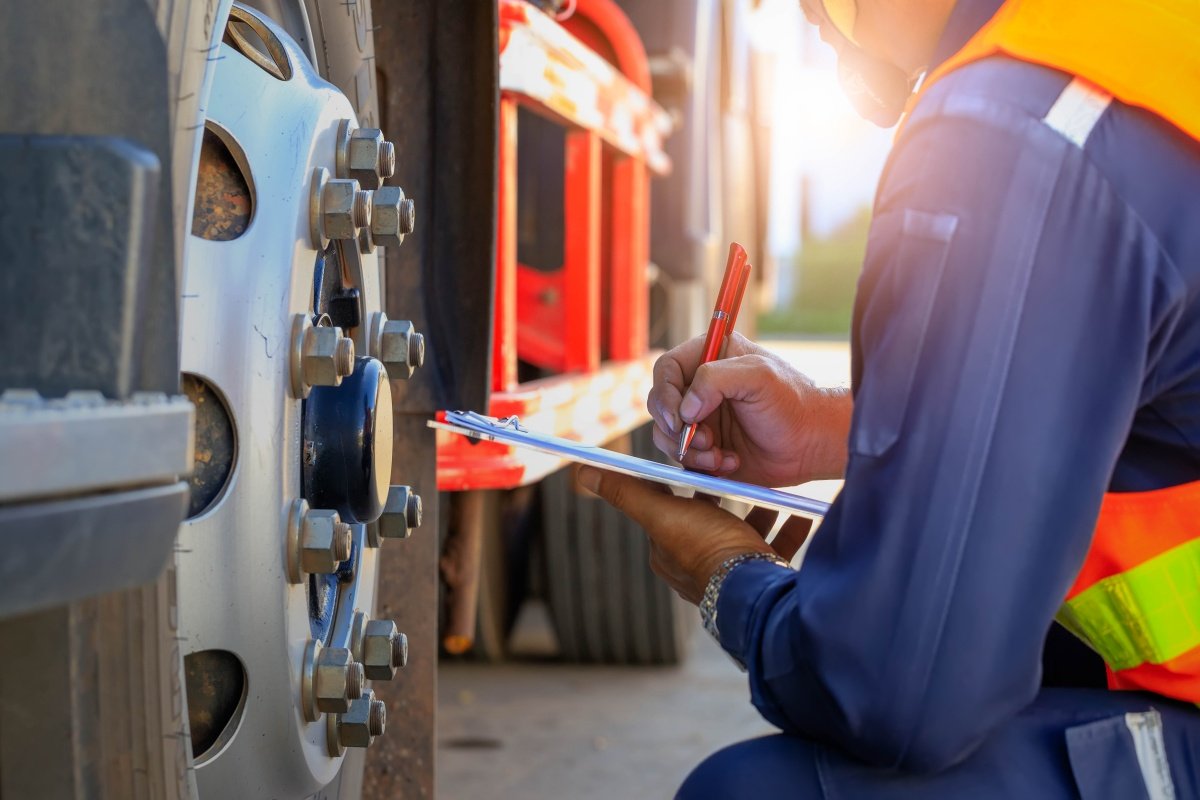
2. Tires and Wheels
Properly maintained tires and wheels improve handling and overall safety on the road. Inspect each tire and wheel assembly carefully before every trip:
- Measure tire pressure with a gauge and compare to the manufacturer’s specifications.
- Check tread depth with a gauge; ensure no exposed cords, cuts, or bulges.
- Inspect sidewalls for cracking, dry rot, or punctures.
- Examine rims for cracks, dents, rust trails, or bent edges.
- Verify lug nuts are tight and look for shiny metal or rust streaks indicating looseness.
- Check wheel seals for visible leaks or residue.
3. Brake System
The brake system requires close attention due to its safety-critical role:
- Inspect air lines and hoses for cuts, wear, and audible leaks.
- Confirm brake chambers are securely mounted, undamaged, and not dented.
- Verify that slack adjusters have proper free play and move as expected.
- Check brake pads or shoes for proper thickness and even wear.
- Inspect push rods, pins, springs, and mounting hardware for missing or loose components.
- Look for brake fluid leaks around calipers, fittings, or lines (if applicable).
4. Lights and Reflectors
Confirm that all lighting and visibility components are operating properly. Missing or malfunctioning lights can lead to citations and increased risk during night or low-visibility driving:
- Test headlights, high beams, taillights, brake lights, and turn signals.
- Check clearance lights, marker lights, and license plate lights for brightness and operation.
- Ensure reflectors on the front, rear, and sides are present, clean, and undamaged.
- Wipe away dirt, snow, or road grime that reduces visibility.
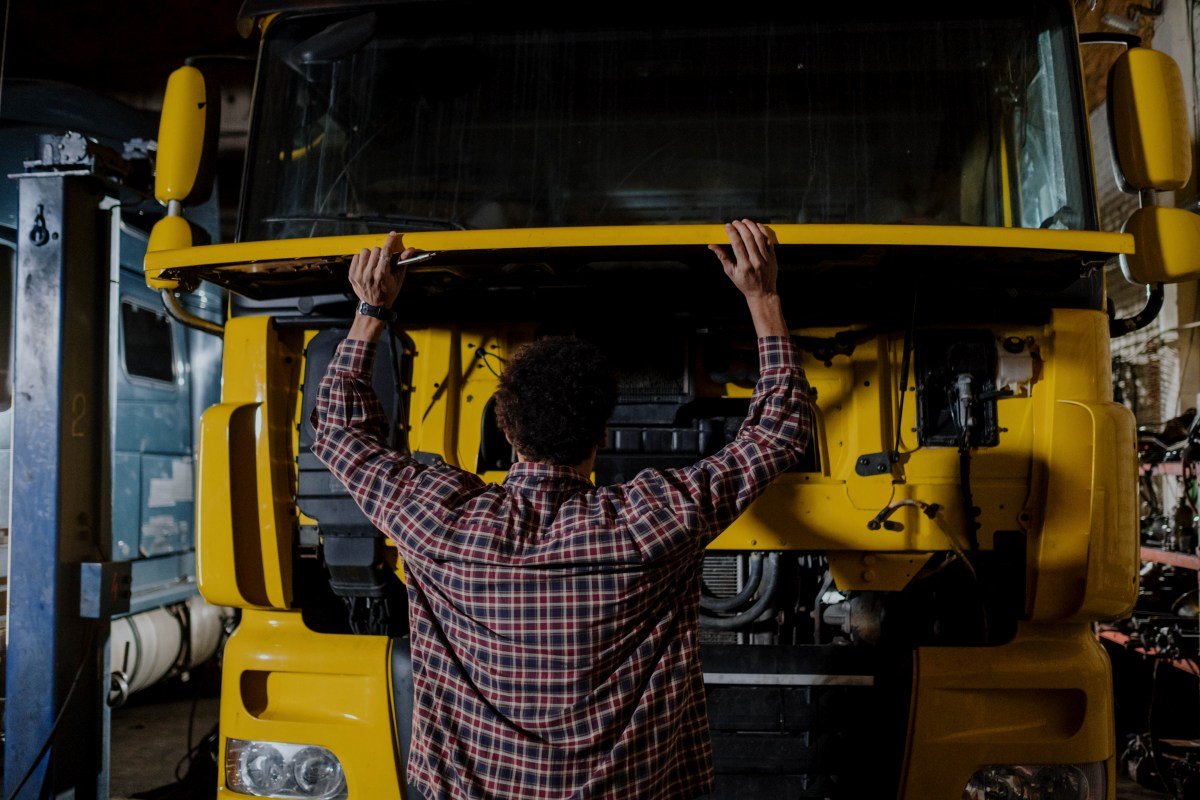
5. Engine Compartment
A clean, leak-free engine compartment reduces breakdowns and improves long-term performance. Inspect the engine compartment with precision:
- Check oil, coolant, brake fluid, and power steering fluid levels.
- Inspect belts for proper tension, fraying, cracks, or glazing.
- Check hoses for soft spots, bulges, cracks, or loose clamps.
- Look for oil, coolant, or fuel leaks around lines, filters, and gaskets.
- Examine mounting brackets, bolts, and engine supports for looseness or damage.
- Inspect the radiator, fan, and shroud for cracks or obstructions.
6. Suspension System
Faulty suspension components impact handling and vehicle stability. Confirm the suspension can safely support your load and maintain stability:
- Inspect leaf springs for cracks, shifted packs, or missing leaves.
- Check shock absorbers for leaks, loose mounts, or excessive wear.
- Verify airbags are holding air, free of punctures, and properly aligned.
- Examine mounts, hangers, and U-bolts for cracks or missing hardware.
7. Steering Components
Any steering abnormality must be addressed immediately to prevent loss of control. Verify the steering system provides full, controlled movement:
- Check the steering gearbox for leaks, secure mounting, and proper connection to the frame.
- Inspect linkages, tie rods, and joints for looseness or worn components.
- Confirm power steering hoses and pump are leak-free.
- Turn the steering wheel to evaluate free play and responsiveness.

8. Fifth Wheel and Coupling Devices
Proper coupling prevents trailer separation, one of the most dangerous failures in trucking. Check the coupling system with extreme accuracy:
- Ensure the locking jaws fully close around the kingpin and cannot move.
- Confirm the release arm is properly seated and locked.
- Inspect the fifth-wheel platform, mounting bolts, and skid plate for cracks or damage.
- Verify grease coverage is sufficient to prevent friction or premature wear.
- Check the kingpin for excessive wear or damage.
9. Trailer and Cargo Securement
Proper cargo securement prevents freight movement, rollovers, and DOT violations. Inspect the trailer and its securement equipment for safety and compliance:
- Check trailer doors, hinges, latches, and locks for full functionality.
- Inspect the trailer floor, walls, and roof for rot, holes, or structural damage.
- Verify that load locks, straps, chains, binders, and winches meet DOT securement standards.
- Ensure cargo is balanced, tightened, and unable to shift.
- Confirm placards, reflectors, and marker lights are present and clean.
10. Exhaust System
A healthy exhaust system prevents fumes from entering the cab and ensures emissions compliance. Make sure the exhaust system is secure and leak-free:
- Inspect pipes, clamps, and mounting brackets for cracks or missing hardware.
- Look for soot trails, which indicate leaks or broken connections.
- Confirm heat shields are intact and not rubbing against components.
11. Fuel System
Fuel system issues can cause fires, breakdowns, or failed inspections. Inspect the fuel system for leaks or contamination risks:
- Check fuel tanks for dents, corrosion, or loose straps.
- Ensure fuel caps seal tightly and the vents function properly.
- Inspect fuel lines for cracks, leaks, or friction points.
- Verify water separators and fuel filters show no signs of contamination.

12. Air and Electrical Lines
Faulty lines impact service brakes, ABS, and lighting, making this step critical. Confirm all connections between the truck and trailer are safe and functional:
- Ensure air lines are connected securely with no audible leaks.
- Inspect glad-hands for proper seals and lubrication.
- Check electrical cables for frayed insulation or exposed wiring.
- Verify the 7-way plug seats are fully seated and power the trailer lights correctly.
13. In-Cab Inspection
A thorough cab inspection ensures you remain comfortable, informed, and compliant on the road. Verify that all cab systems and safety components function properly:
- Check seat belts for secure latching and visible wear.
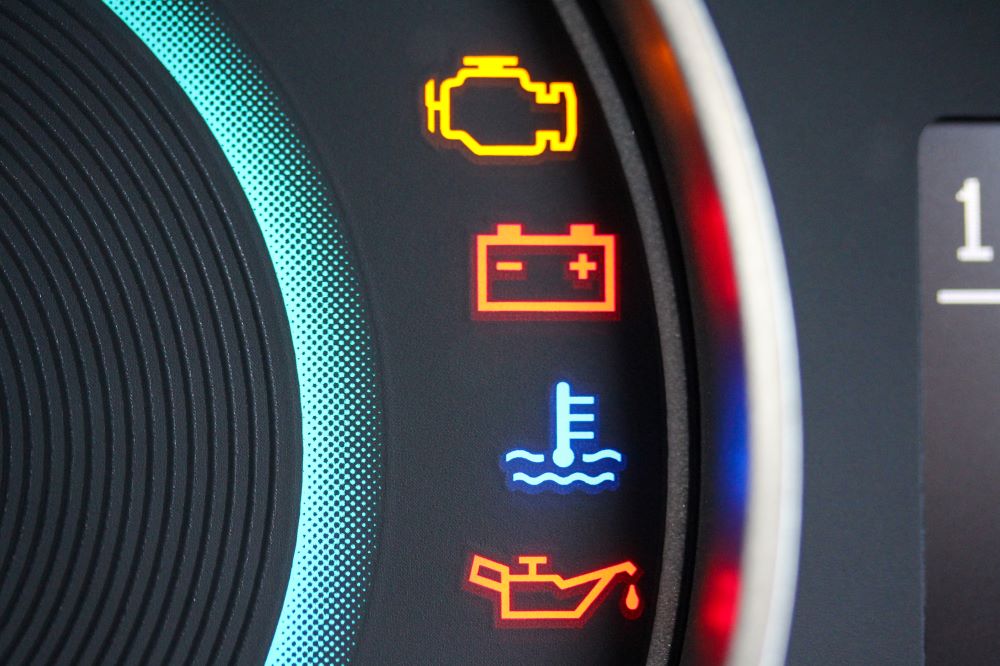
- Start the truck and confirm gauges (oil pressure, temperature, air pressure, voltage) reach normal operating ranges.
- Test the horn, windshield wipers, and washer fluid.
- Confirm the heater, defroster, and AC work correctly.
- Adjust mirrors and ensure the cab is free of loose items that could interfere with driving.
- Verify all warning lights and indicator lamps operate correctly during start-up.
14. Emergency Equipment
Emergency equipment ensures you can safely respond to breakdowns or hazardous conditions. Ensure all emergency tools meet DOT requirements and are ready for use:
- Check the fire extinguisher for proper charge, secure mounting, and accessibility.
- Confirm reflective triangles are present and undamaged.
- Verify fuses or circuit breakers are available for electrical repairs.
- Inspect any first-aid kits or additional safety items required by your carrier.
Conclusion
A comprehensive checklist helps drivers operate safely, avoid violations, and stay ahead of mechanical issues that could lead to costly repairs.
By examining each component (tires, brakes, lights, engine compartment, trailer, and in-cab systems), you ensure your truck is road-ready and fully compliant with industry standards.
If your truck needs financing for repairs or replacement equipment, Mission Financial Services can help.
We provide direct lending solutions designed specifically for owner-operators and small fleets, including bad credit loans, repair loans, first-time buyer programs, and more.
If you’re preparing your vehicle for the road and need reliable financing support, Mission Financial Services is ready to help you keep your business moving. Start your credit application today.